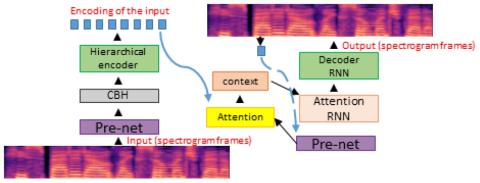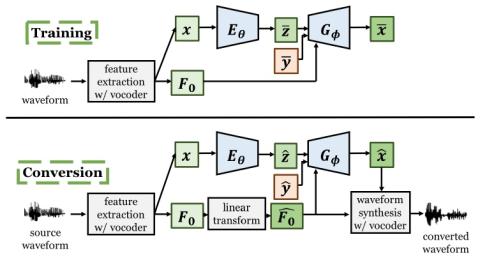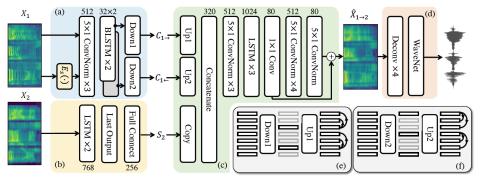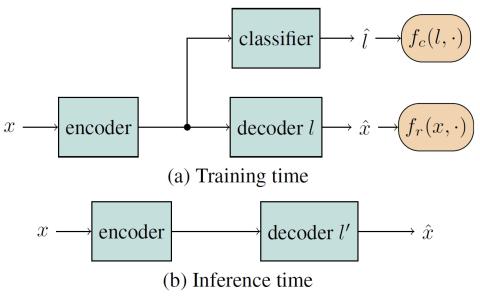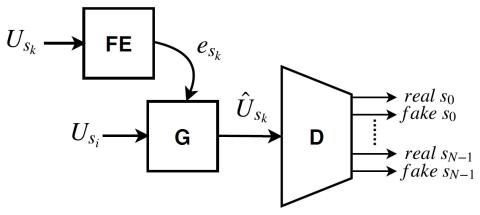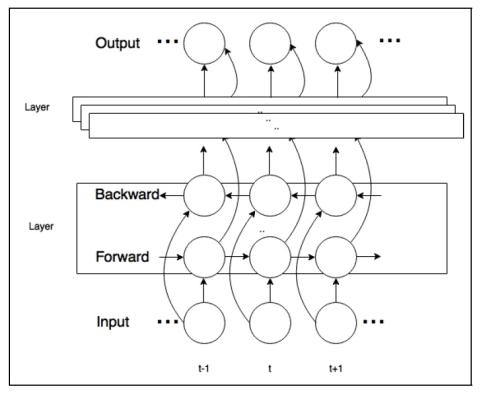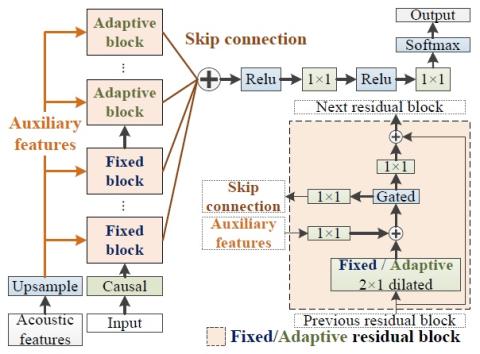
Statistical Voice Conversion with Quasi-Periodic WaveNet Vocoder
In this paper, we investigate the effectiveness of a quasi-periodic WaveNet (QPNet) vocoder combined with a statistical spectral conversion technique for a voice conversion task. The WaveNet (WN) vocoder has been applied as the waveform generation module in many different voice conversion frameworks and achieves significant improvement over conventional vocoders. However, because of the fixed dilated convolution and generic network architecture, the WN vocoder lacks robustness against unseen input features and often requires a huge network size to achieve acceptable speech quality. Such limita...