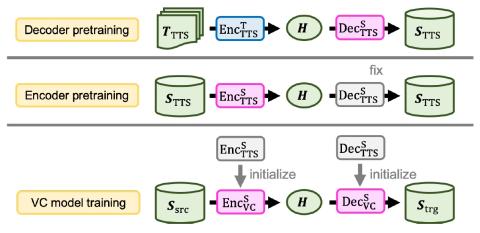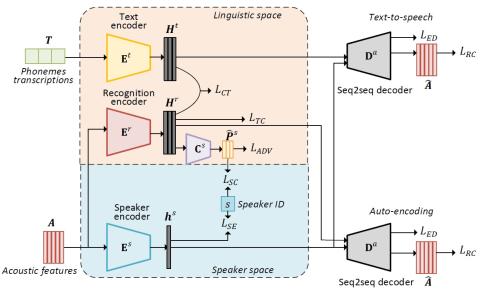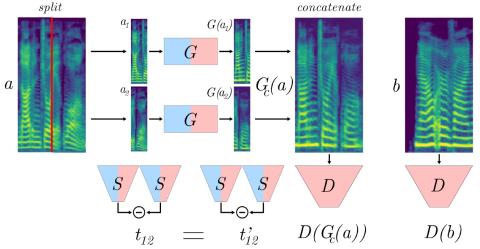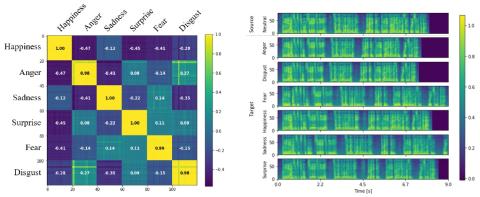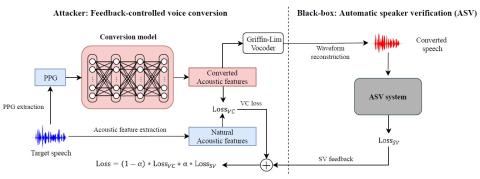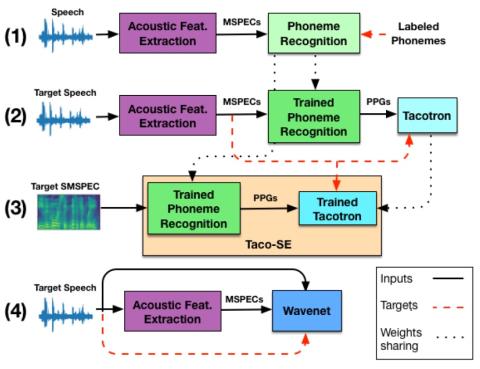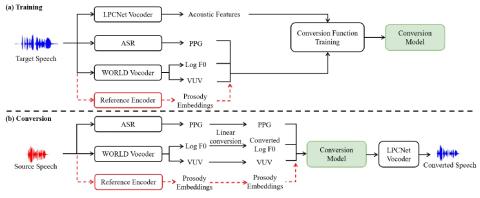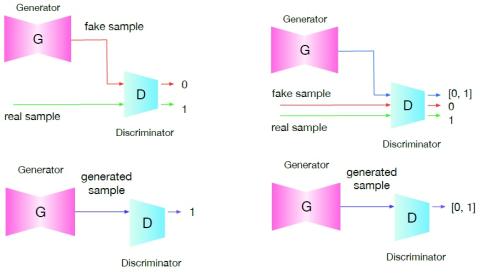
MoEVC: A Mixture-of-experts Voice Conversion System with Sparse Gating Mechanism for Accelerating Online Computation
With the recent advancements of deep learning technologies, the performance of voice conversion (VC) in terms of quality and similarity has been significantly improved. However, heavy computations are generally required for deep-learning-based VC systems, which can cause notable latency and thus confine their deployments in real-world applications. Therefore, increasing online computation efficiency has become an important task. In this study, we propose a novel mixture-of-experts (MoE) based VC system. The MoE model uses a gating mechanism to specify optimal weights to feature maps to increas...