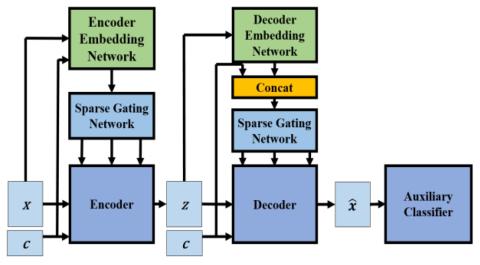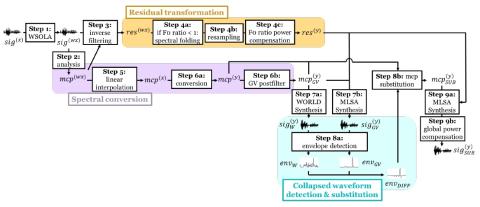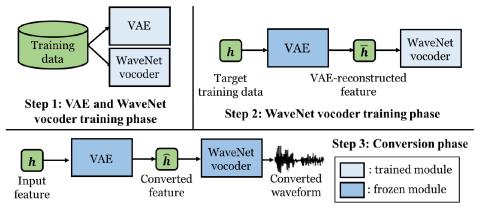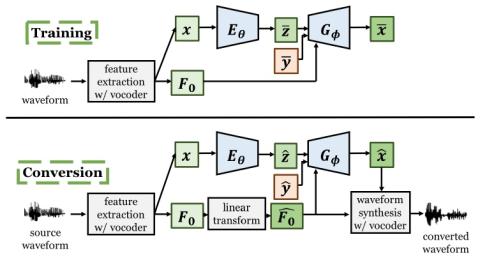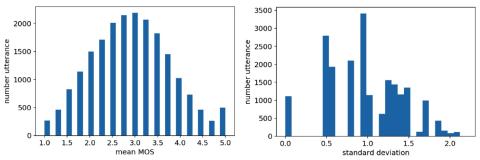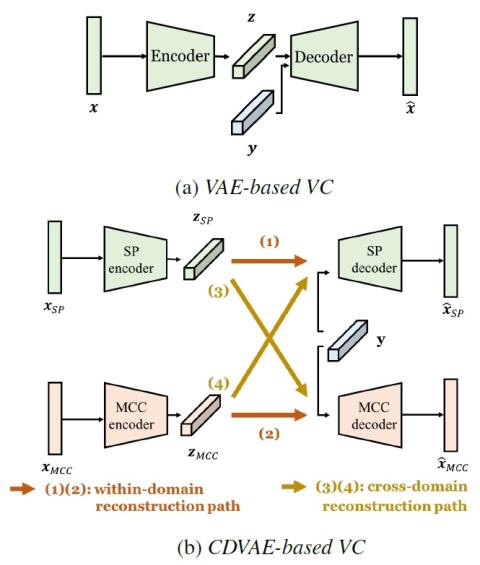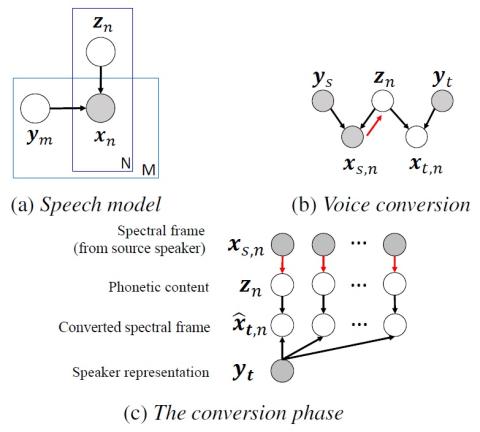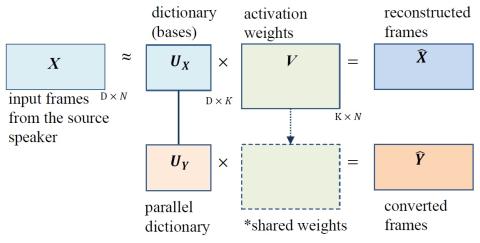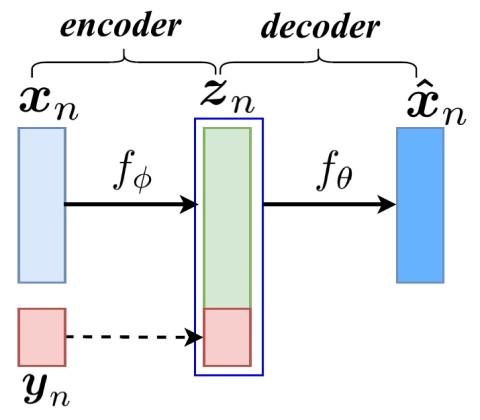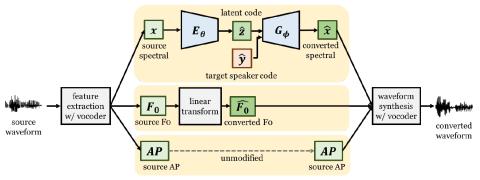
Unsupervised Representation Disentanglement using Cross Domain Features and Adversarial Learning in Variational Autoencoder based Voice Conversion
An effective approach for voice conversion (VC) is to disentangle linguistic content from other components in the speech signal. The effectiveness of variational autoencoder (VAE) based VC (VAE-VC), for instance, strongly relies on this principle. In our prior work, we proposed a cross-domain VAE-VC (CDVAE-VC) framework, which utilized acoustic features of different properties, to improve the performance of VAE-VC. We believed that the success came from more disentangled latent representations. In this paper, we extend the CDVAE-VC framework by incorporating the concept of adversarial learning...