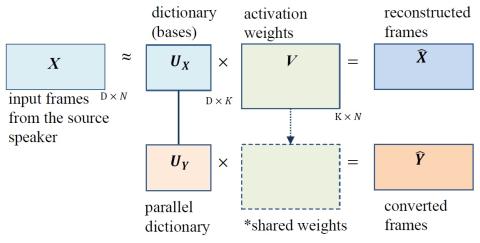
In this paper, we propose a dictionary update method for Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (NMF) with high dimensional data in a spectral conversion (SC) task. Voice conversion has been widely studied due to its potential applications such as personalized speech synthesis and speech enhancement. Exemplar-based NMF (ENMF) emerges as an effective and probably the simplest choice among all techniques for SC, as long as a source-target parallel speech corpus is given. ENMF-based SC systems usually need a large amount of bases (exemplars) to ensure the quality of the converted speech. However, a small and effective dictionary is desirable but hard to obtain via dictionary update, in particular when high-dimensional features such as STRAIGHT spectra are used. Therefore, we propose a dictionary update framework for NMF by means of an encoder-decoder reformulation. Regarding NMF as an encoder-decoder network makes it possible to exploit the whole parallel corpus more effectively and efficiently when applied to SC. Our experiments demonstrate significant gains of the proposed system with small dictionaries over conventional ENMF-based systems with dictionaries of same or much larger size.
Conclusions
This paper has presented a dictionary update framework for NMF-based spectral conversion by reformulating NMF as an encoder-decoder network. The merits are two-fold. First, the proposed method avoids explicit joint dictionary update that doubles the dimensionality. Second, the learned dictionary is much more compact and has a higher representational power, resulting in better voice quality in the converted speech. The encoder-decoder network formulation can be easily generalized to application cases without the non-negativity constraint. We will consider these cases in the future.