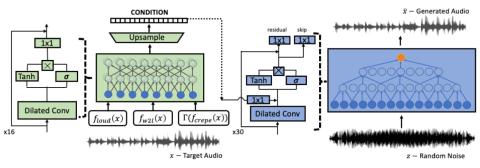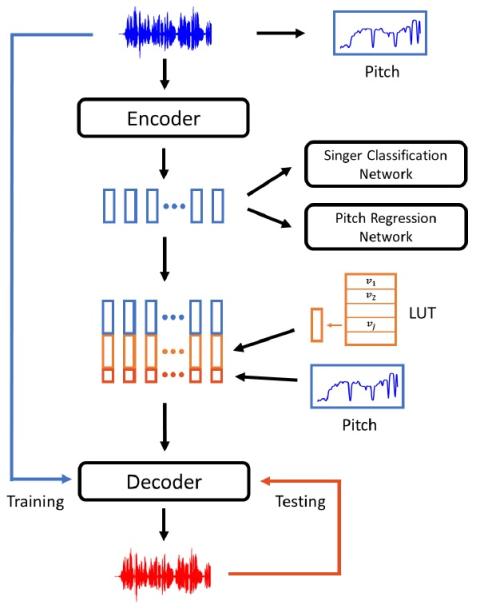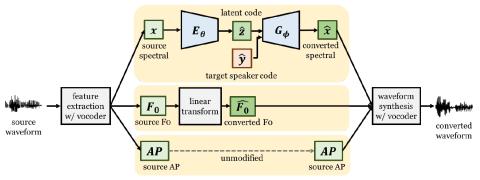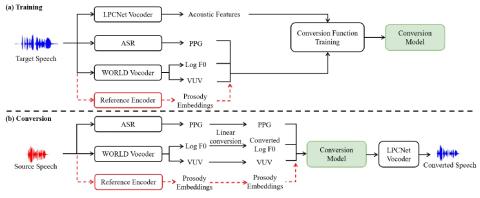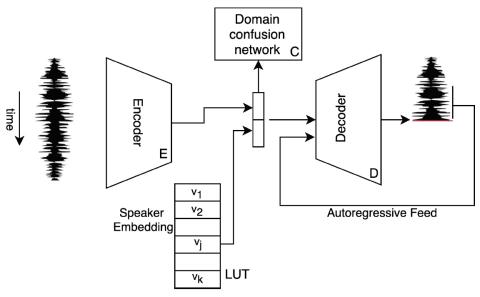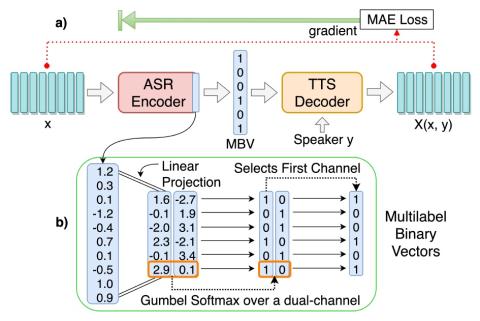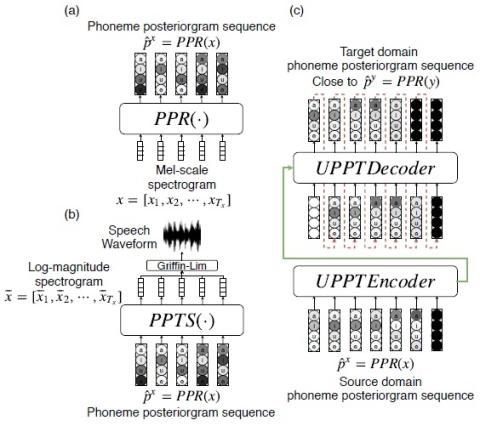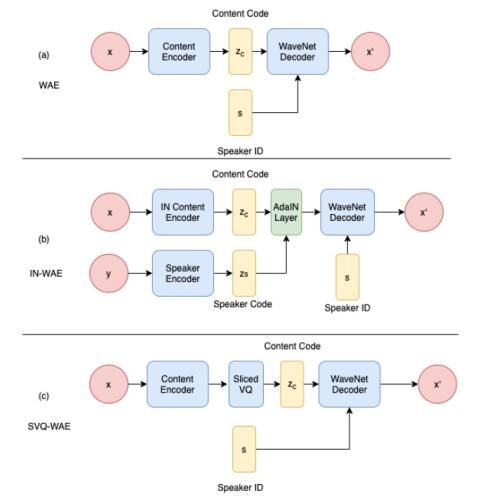
Unsupervised Acoustic Unit Representation Learning for Voice Conversion using WaveNet Auto-encoders
Unsupervised representation learning of speech has been of keen interest in recent years, which is for example evident in the wide interest of the ZeroSpeech challenges. This work presents a new method for learning frame level representations based on WaveNet auto-encoders. Of particular interest in the ZeroSpeech Challenge 2019 were models with discrete latent variable such as the Vector Quantized Variational Auto-Encoder (VQVAE). However these models generate speech with relatively poor quality. In this work we aim to address this with two approaches: first WaveNet is used as the decoder and...