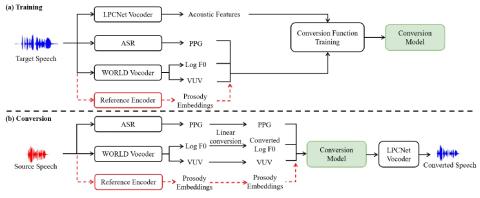
In a typical voice conversion system, prior works utilize various acoustic features (e.g., the pitch, voiced/unvoiced flag, aperiodicity) of the source speech to control the prosody of generated waveform. However, the prosody is related with many factors, such as the intonation, stress and rhythm. It is a challenging task to perfectly describe the prosody through acoustic features. To deal with this problem, we propose prosody embeddings to model prosody. These embeddings are learned from the source speech in an unsupervised manner. We conduct experiments on our Mandarin corpus recoded by professional speakers. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method enables fine-grained control of the prosody. In challenging situations (such as the source speech is a singing song), our proposed method can also achieve promising results.
Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a voice conversion framework based on prosody embeddings and LPCNet. The prosody embeddings enable fine-grained control of the prosody of generated speech. LPCNet can synthesize speech with close to natural quality while running in real time on a standard CPU. Subjective evaluations show that the proposed method can achieve both high naturalness and high speaker similarity in challenging situations, such as the source speech is a singing song.