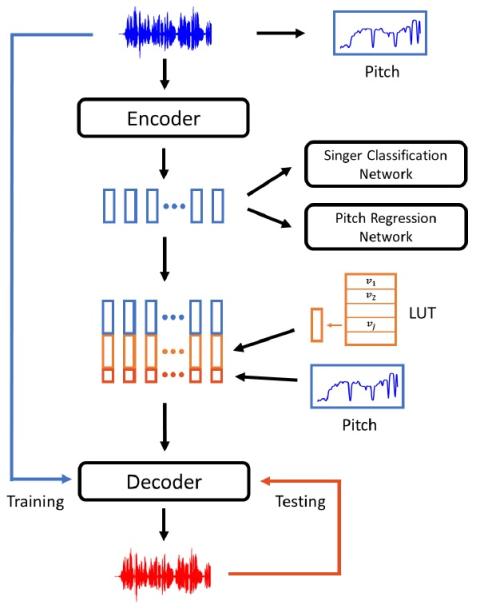
Singing voice conversion is to convert a singer's voice to another one's voice without changing singing content. Recent work shows that unsupervised singing voice conversion can be achieved with an autoencoder-based approach [1]. However, the converted singing voice can be easily out of key, showing that the existing approach cannot model the pitch information precisely. In this paper, we propose to advance the existing unsupervised singing voice conversion method proposed in [1] to achieve more accurate pitch translation and flexible pitch manipulation. Specifically, the proposed PitchNet added an adversarially trained pitch regression network to enforce the encoder network to learn pitch invariant phoneme representation, and a separate module to feed pitch extracted from the source audio to the decoder network. Our evaluation shows that the proposed method can greatly improve the quality of the converted singing voice (2.92 vs 3.75 in MOS). We also demonstrate that the pitch of converted singing can be easily controlled during generation by changing the levels of the extracted pitch before passing it to the decoder network.
Conclusion
In this paper, a novel unsupervised singing voice conversion method named PitchNet is proposed. A pitch regression network is employed to render an adversarial loss separating pitch related information from the latent space in autoencoder. After the WaveNet-like encoder, a singer and pitch invariant representation is generated and then fed into theWaveNet decoder conditioning on the singer embedding and the extracted pitch to reconstruct the target singing voice. Our method outperforms the existing unsupervised singing voice conversion method and achieves flexible pitch manipulation.