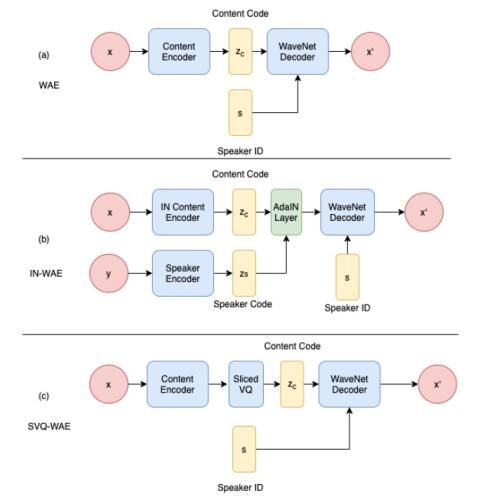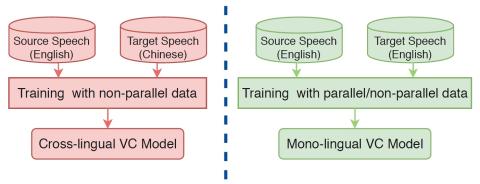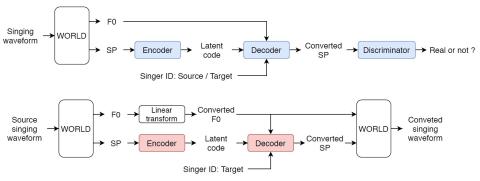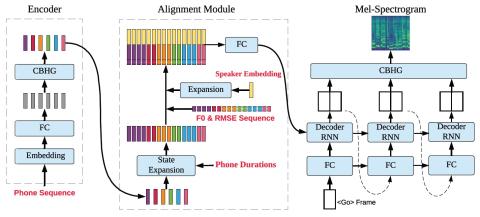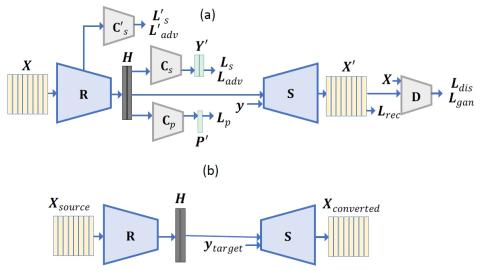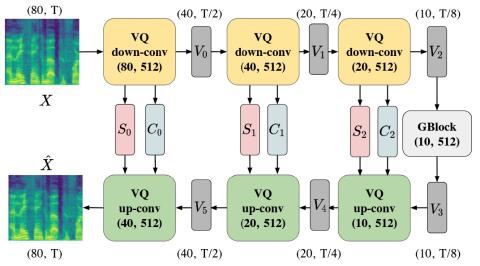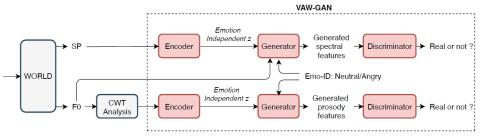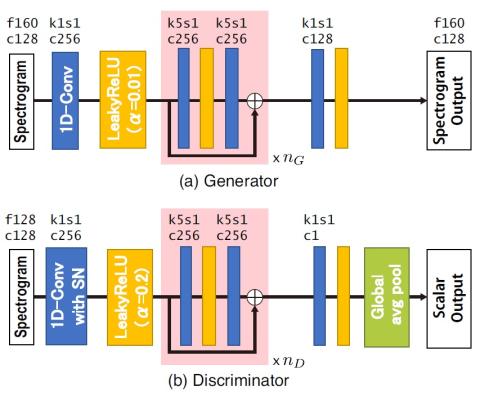
Nonparallel Voice Conversion with Augmented Classifier Star Generative Adversarial Networks
We have previously proposed a method that allows for non-parallel voice conversion (VC) by using a variant of generative adversarial networks (GANs) called StarGAN. The main features of our method, called StarGAN-VC, are as follows: First, it requires no parallel utterances, transcriptions, or time alignment procedures for speech generator training. Second, it can simultaneously learn mappings across multiple domains using a single generator network so that it can fully exploit available training data collected from multiple domains to capture latent features that are common to all the domains...