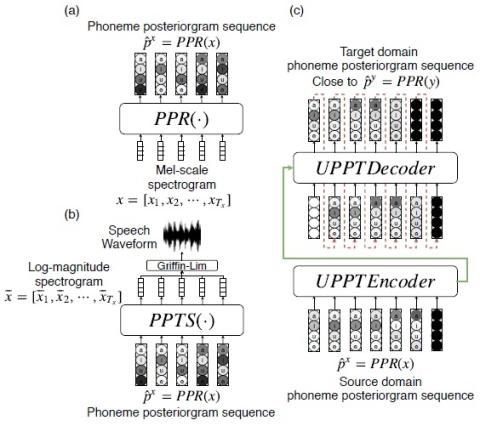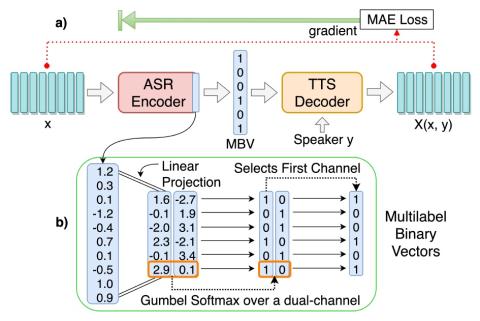
Unsupervised End-to-End Learning of Discrete Linguistic Units for Voice Conversion
We present an unsupervised end-to-end training scheme where we discover discrete subword units from speech without using any labels. The discrete subword units are learned under an ASR-TTS autoencoder reconstruction setting, where an ASR-Encoder is trained to discover a set of common linguistic units given a variety of speakers, and a TTS-Decoder trained to project the discovered units back to the designated speech. We propose a discrete encoding method, Multilabel-Binary Vectors (MBV), to make the ASR-TTS autoencoder differentiable. We found that the proposed encoding method offers automatic ...