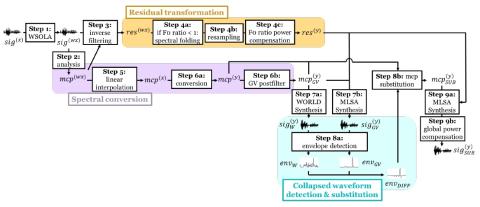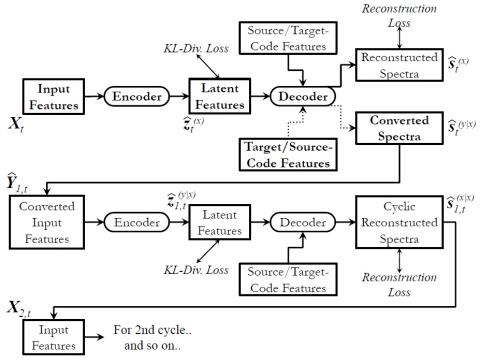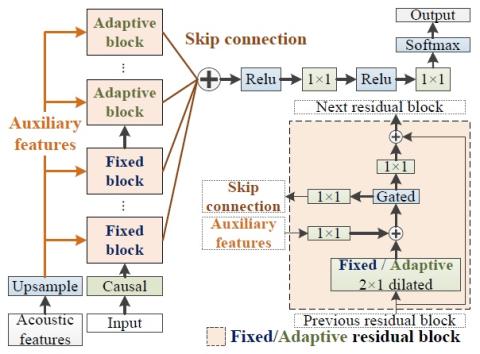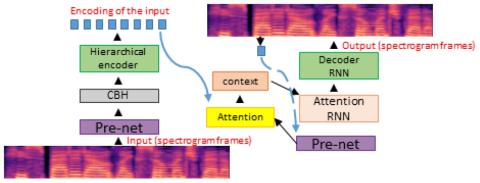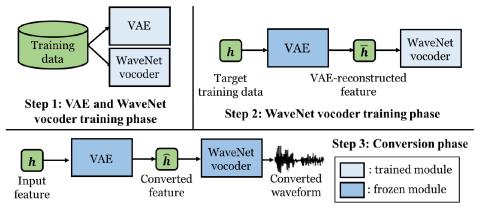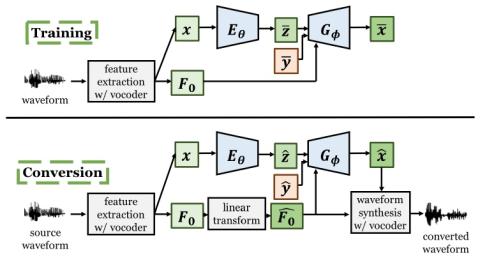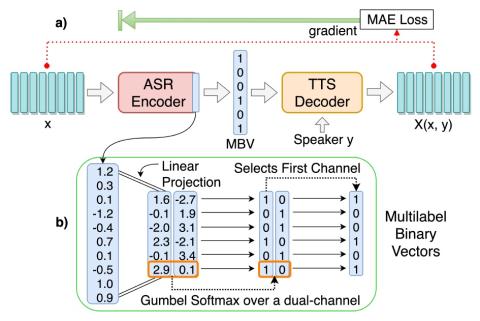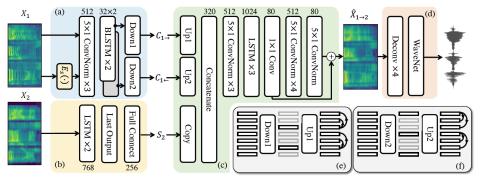
V2S attack: building DNN-based voice conversion from automatic speaker verification
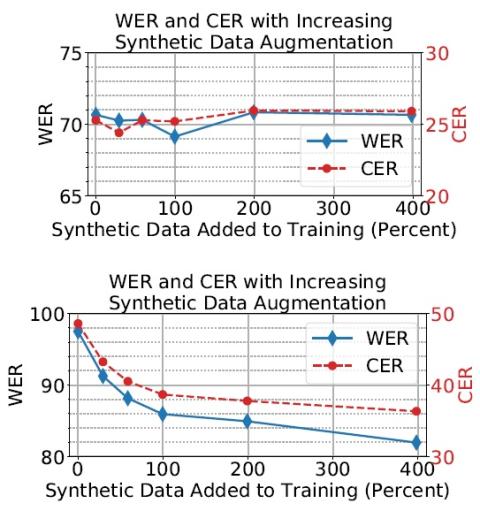
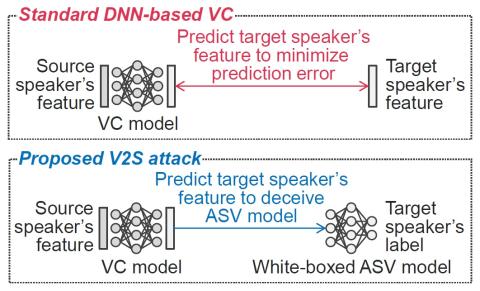
This paper presents a new voice impersonation attack using voice conversion (VC). Enrolling personal voices for automatic speaker verification (ASV) offers natural and flexible biometric authentication systems. Basically, the ASV systems do not include the users' voice data. However, if the ASV system is unexpectedly exposed and hacked by a malicious attacker, there is a risk that the attacker will use VC techniques to reproduce the enrolled user's voices. We name this the verification-to-synthesis (V2S) attack'' and propose VC training with the ASV and pre-trained automatic speech recognition...