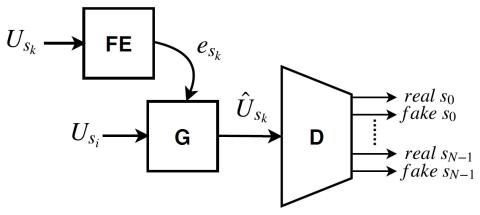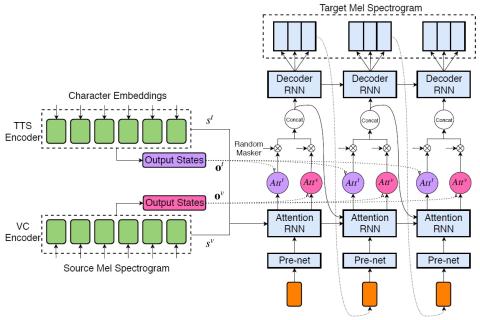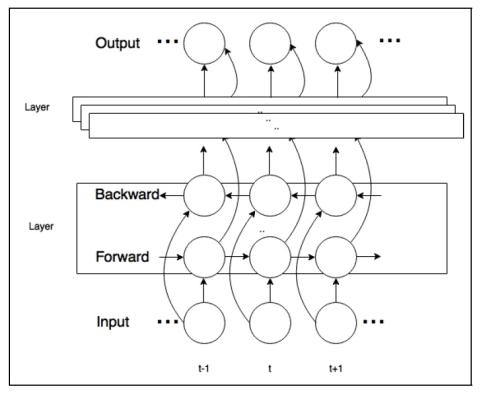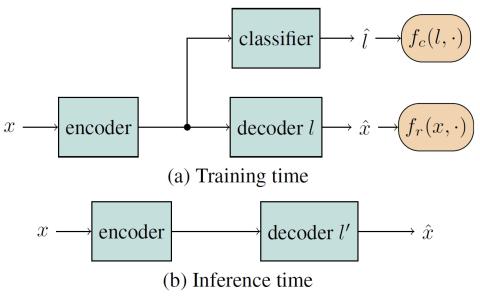
Adversarially Trained Autoencoders for Parallel-Data-Free Voice Conversion
We present a method for converting the voices between a set of speakers. Our method is based on training multiple autoencoder paths, where there is a single speaker-independent encoder and multiple speaker-dependent decoders. The autoencoders are trained with an addition of an adversarial loss which is provided by an auxiliary classifier in order to guide the output of the encoder to be speaker independent. The training of the model is unsupervised in the sense that it does not require collecting the same utterances from the speakers nor does it require time aligning over phonemes. Due to the ...