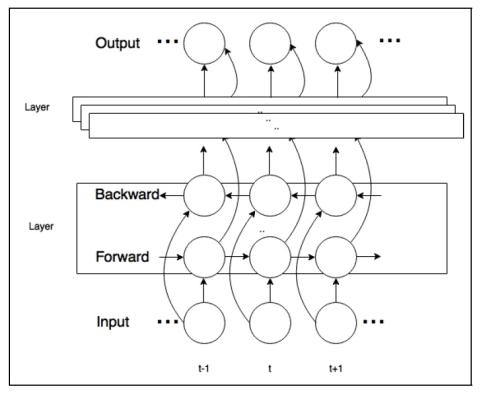
Singing voice conversion is a task to convert a song sang by a source singer to the voice of a target singer. In this paper, we propose using a parallel data free, many-to-one voice conversion technique on singing voices. A phonetic posterior feature is first generated by decoding singing voices through a robust Automatic Speech Recognition Engine (ASR). Then, a trained Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) with a Deep Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (DBLSTM) structure is used to model the mapping from person-independent content to the acoustic features of the target person. F0 and aperiodic are obtained through the original singing voice, and used with acoustic features to reconstruct the target singing voice through a vocoder. In the obtained singing voice, the targeted and sourced singers sound similar. To our knowledge, this is the first study that uses non parallel data to train a singing voice conversion system. Subjective evaluations demonstrate that the proposed method effectively converts singing voices.
Conclusion
We propose a novel system to use a parallel data free, many-to-one voice conversion on singing voice conversion. A speaker independent ASR is first used to extract the phonetic posteriors sequence to represent the person-independent content, and a DBLSTM model is used to model the mapping from the person-independent content to target speaker’s acoustic features. These acoustic features are used to synthesize the target singing voice via a vocoder, together with the F0 and aperiodic information extracted from the source content.
To our knowledge, this is the first attempt to use nonparallel data to train a model for singing voice conversion. Additionally, subjective evaluation reveals that the proposed method is effective without using parallel data.
For future enhancement, the authors would like to collect more singing voice data for model adaptation in speech recognition to further improve performance. In our future work, we also hope to explore neural vocoders such as wavenet, a recently proposed method that demonstrates superior performance when compared to traditional vocoders.