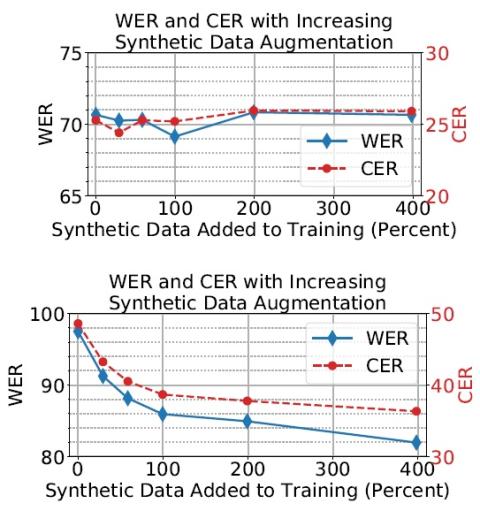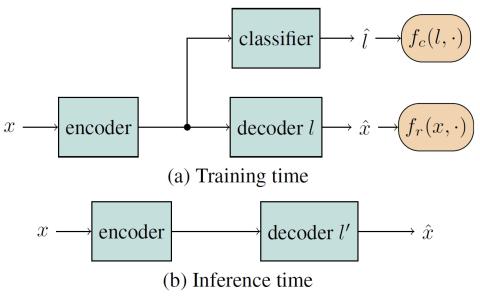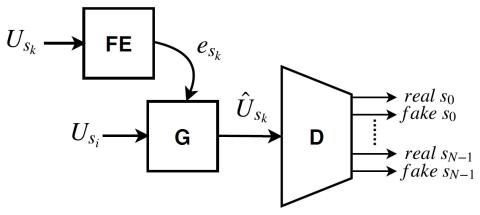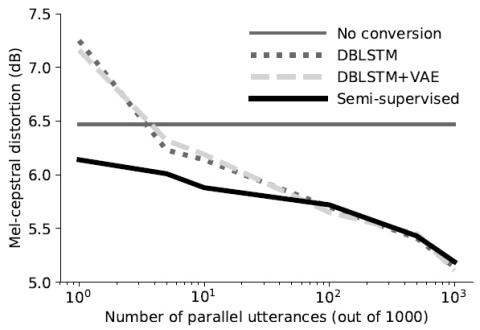
Semi-supervised voice conversion with amortized variational inference
In this work we introduce a semi-supervised approach to the voice conversion problem, in which speech from a source speaker is converted into speech of a target speaker. The proposed method makes use of both parallel and non-parallel utterances from the source and target simultaneously during training. This approach can be used to extend existing parallel data voice conversion systems such that they can be trained with semi-supervision. We show that incorporating semi-supervision improves the voice conversion performance compared to fully supervised training when the number of parallel utteran...