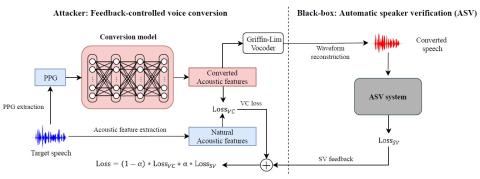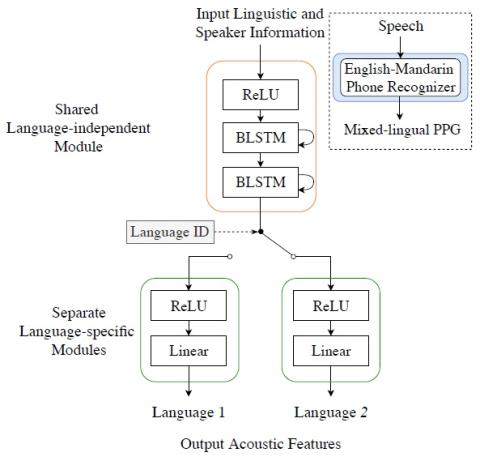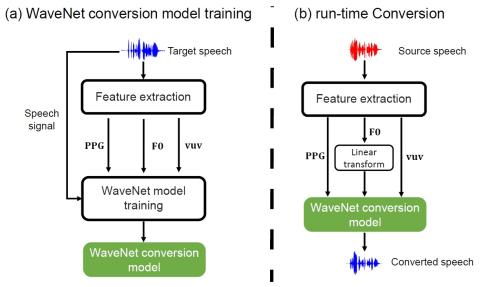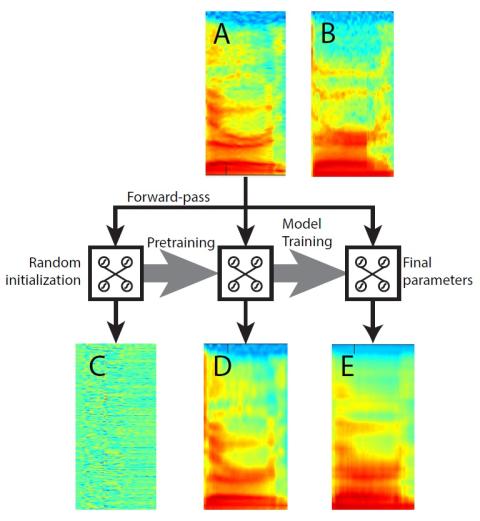
Voice Conversion Challenge 2020: Intra-lingual semi-parallel and cross-lingual voice conversion
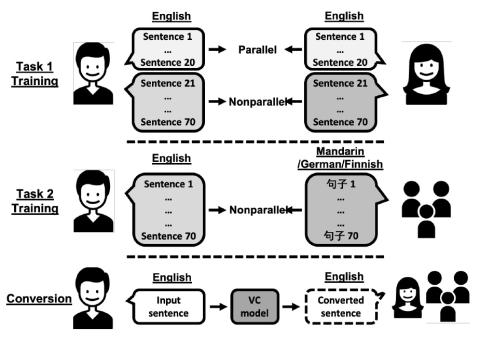
The voice conversion challenge is a bi-annual scientific event held to compare and understand different voice conversion (VC) systems built on a common dataset. In 2020, we organized the third edition of the challenge and constructed and distributed a new database for two tasks, intra-lingual semi-parallel and cross-lingual VC. After a two-month challenge period, we received 33 submissions, including 3 baselines built on the database. From the results of crowd-sourced listening tests, we observed that VC methods have progressed rapidly thanks to advanced deep learning methods. In particular, s...