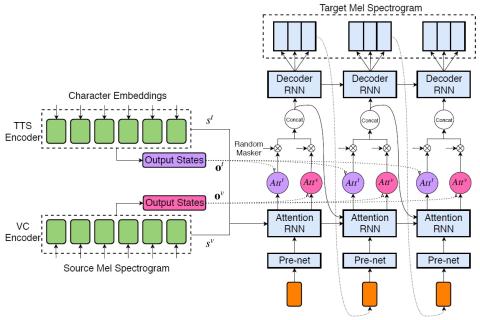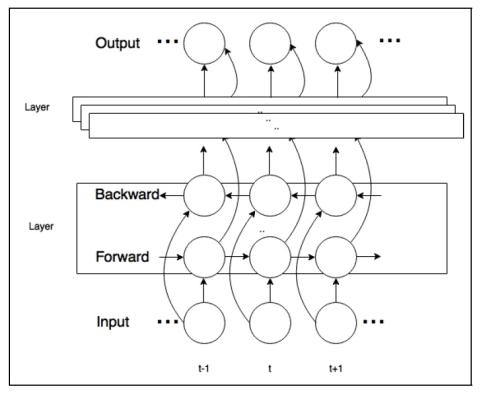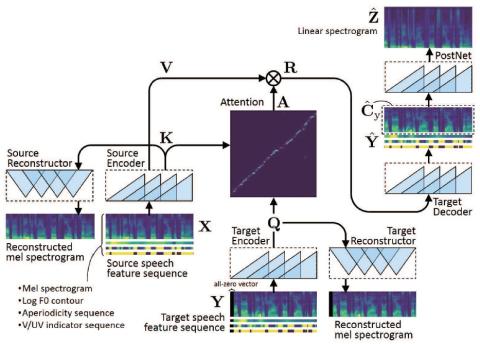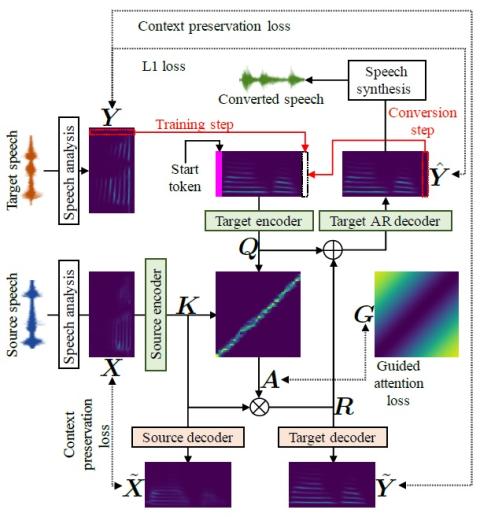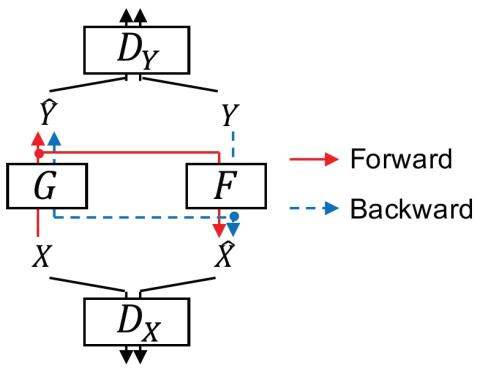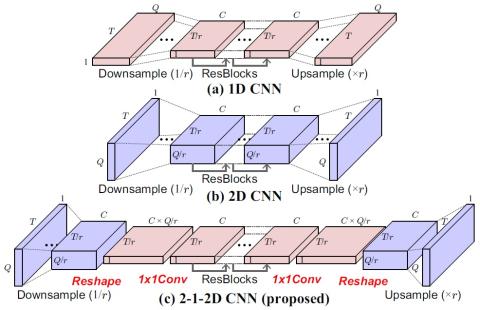
CycleGAN-VC2: Improved CycleGAN-based Non-parallel Voice Conversion
Non-parallel voice conversion (VC) is a technique for learning the mapping from source to target speech without relying on parallel data. This is an important task, but it has been challenging due to the disadvantages of the training conditions. Recently, CycleGAN-VC has provided a breakthrough and performed comparably to a parallel VC method without relying on any extra data, modules, or time alignment procedures. However, there is still a large gap between the real target and converted speech, and bridging this gap remains a challenge. To reduce this gap, we propose CycleGAN-VC2, which is an...