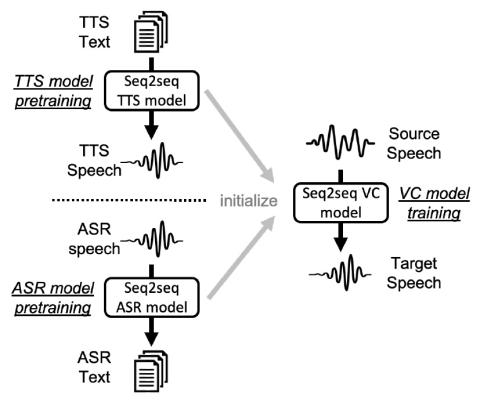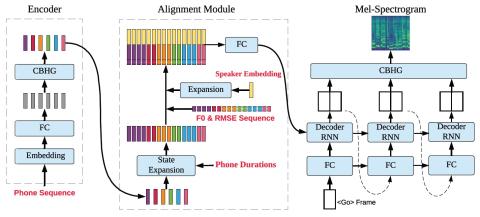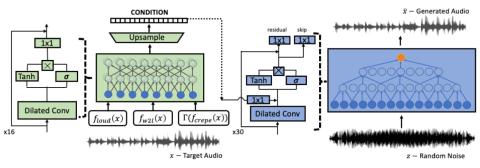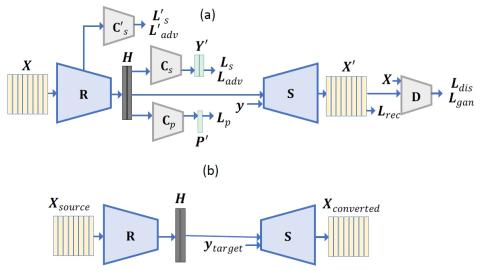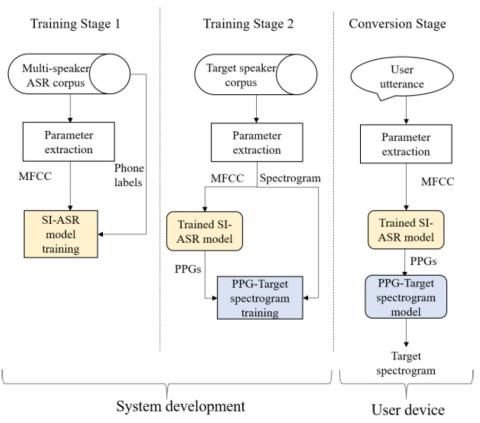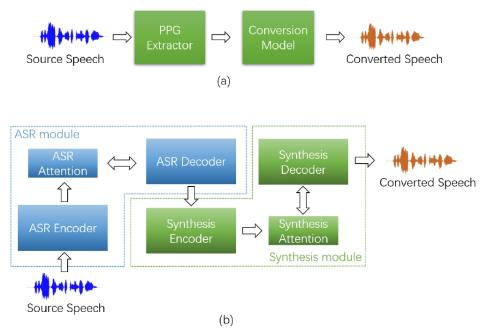
Any-to-Many Voice Conversion with Location-Relative Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling
This paper proposes an any-to-many location-relative, sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq), non-parallel voice conversion approach, which utilizes text supervision during training. In this approach, we combine a bottle-neck feature extractor (BNE) with a seq2seq synthesis module. During the training stage, an encoder-decoder-based hybrid connectionist-temporal-classification-attention (CTC-attention) phoneme recognizer is trained, whose encoder has a bottle-neck layer. A BNE is obtained from the phoneme recognizer and is utilized to extract speaker-independent, dense and rich spoken content represen...