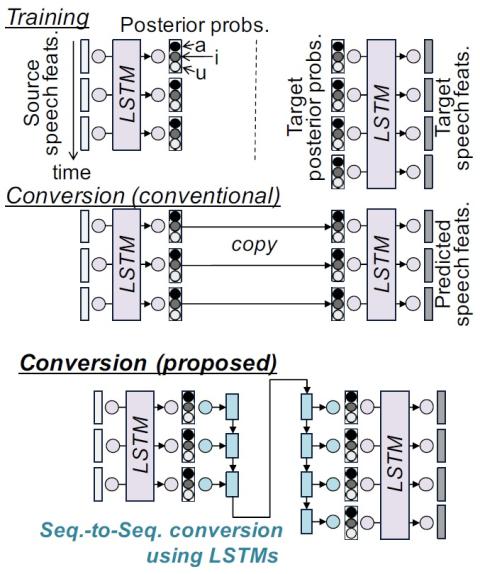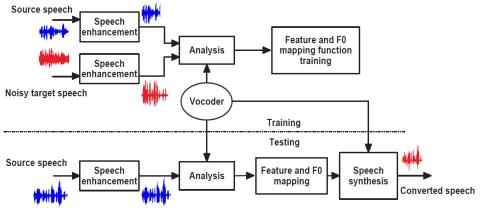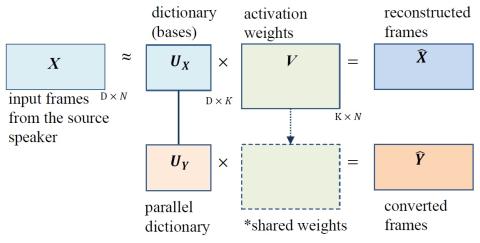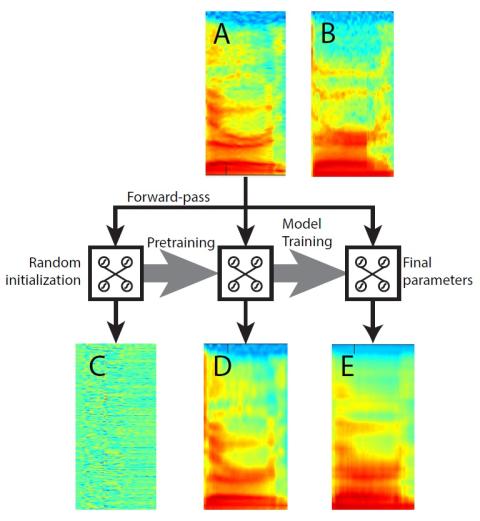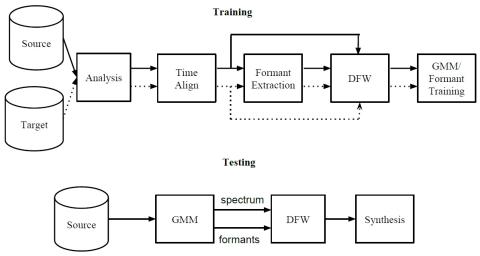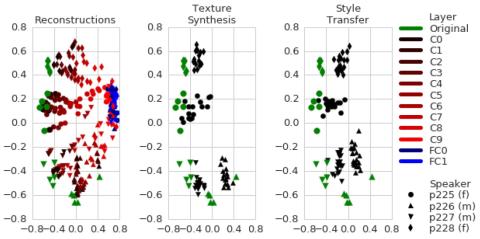
On Using Backpropagation for Speech Texture Generation and Voice Conversion
Inspired by recent work on neural network image generation which rely on backpropagation towards the network inputs, we present a proof-of-concept system for speech texture synthesis and voice conversion based on two mechanisms: approximate inversion of the representation learned by a speech recognition neural network, and on matching statistics of neuron activations between different source and target utterances. Similar to image texture synthesis and neural style transfer, the system works by optimizing a cost function with respect to the input waveform samples. To this end we use a differen...