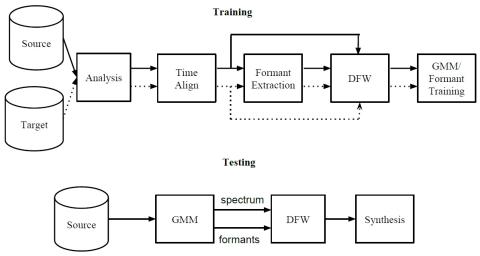
In this study, we investigate a solution to reduce the effect of one-to-many problem in voice conversion. One-to-many problem in VC happens when two very similar speech segments in source speaker have corresponding speech segments in target speaker that are not similar to each other. As a result, the mapper function usually over-smoothes the generated features in order to be similar to both target speech segments. In this study, we propose to equalize the formant location of source-target frame pairs using dynamic frequency warping in order to reduce the complexity. After the conversion, another dynamic frequency warping is further applied to reverse the effect of formant location equalization during the training. The subjective experiments showed that the proposed approach improves the speech quality significantly.
Conclusion
In this study, we investigated a solution to reduce the effect of one-to-many problem in voice conversion. We proposed to equalize the formant location of source-target frame pairs using dynamic frequency warping in order to reduce the complexity. Finally, A dynamic frequency warping is further applied after the conversion to reverse the effect of formant location equalization. We were able to show a significant gain in speech quality. Two issues present themselves here. The issue is using DFW directly on the log-spectrum domain, which might cause distorted-looking spectra, specially if there is a formant error. For controlling for this problem, using other warping approaches such as pole-shifting might be helpful. The other more important problem is the formant estimation mismatches that are inevitable. For solving this problem, hand-corrected formant values can be used for experimentation purposes to see the real effect of the proposed approach with the ground truth formant information.