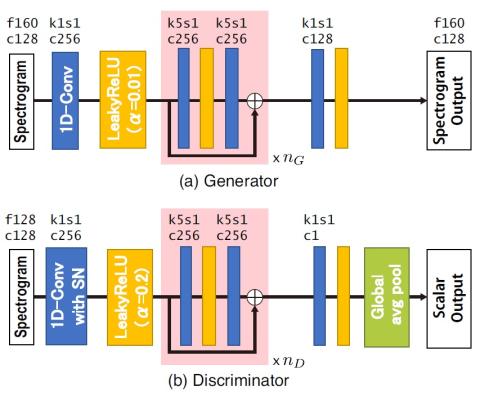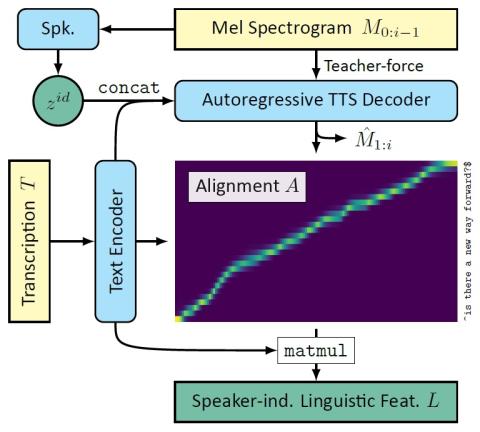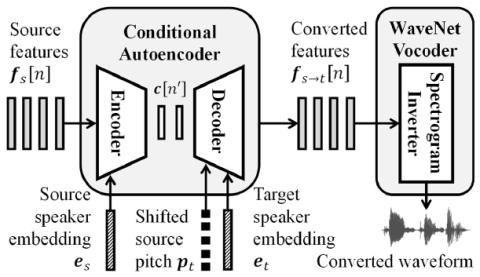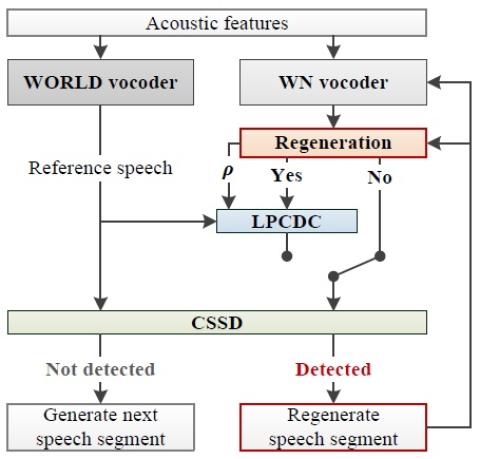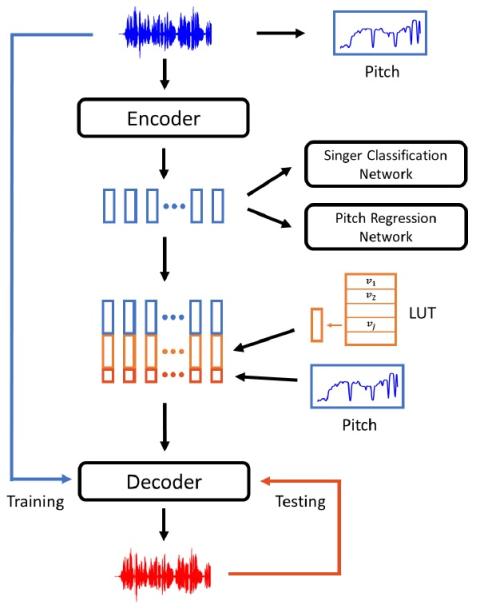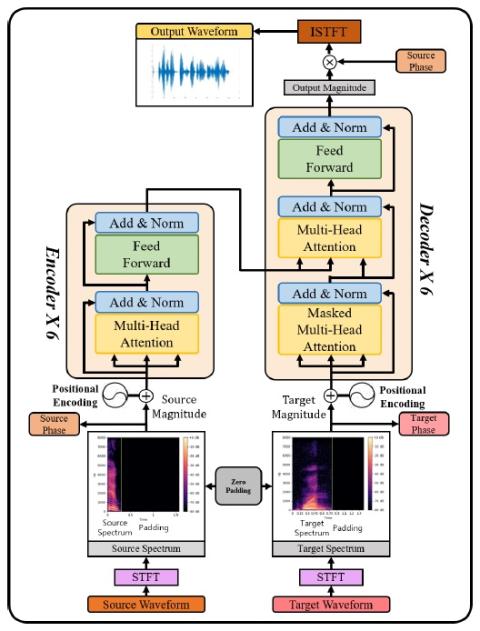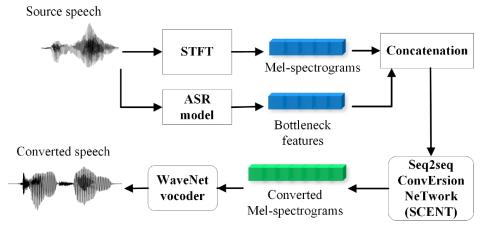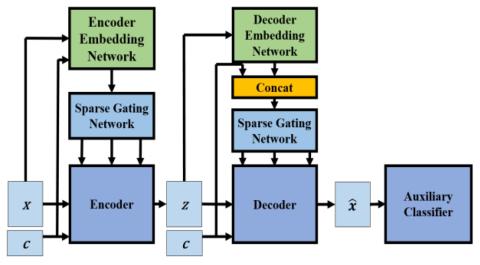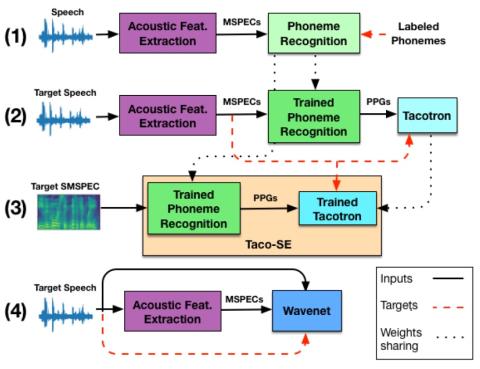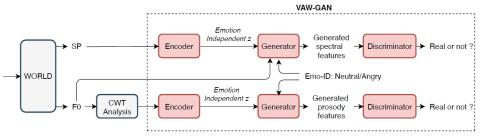
Converting Anyone's Emotion: Towards Speaker-Independent Emotional Voice Conversion
Emotional voice conversion aims to convert the emotion of the speech from one state to another while preserving the linguistic content and speaker identity. The prior studies on emotional voice conversion are mostly carried out under the assumption that emotion is speaker-dependent. We believe that emotions are expressed universally across speakers, therefore, the speaker-independent mapping between emotional states of speech is possible. In this paper, we propose to build a speaker-independent emotional voice conversion framework, that can convert anyone's emotion without the need for paralle...