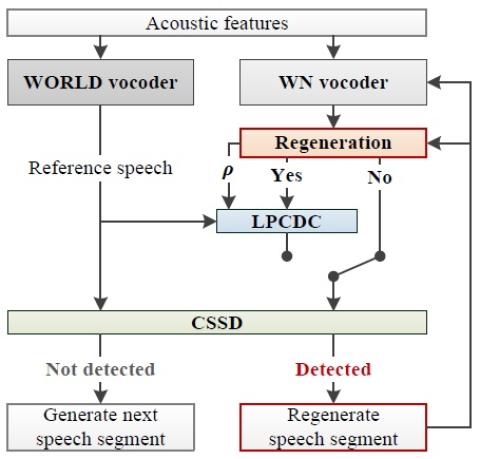
In this paper, we integrate a simple non-parallel voice conversion (VC) system with a WaveNet (WN) vocoder and a proposed collapsed speech suppression technique. The effectiveness of WN as a vocoder for generating high-fidelity speech waveforms on the basis of acoustic features has been confirmed in recent works. However, when combining the WN vocoder with a VC system, the distorted acoustic features, acoustic and temporal mismatches, and exposure bias usually lead to significant speech quality degradation, making WN generate some very noisy speech segments called collapsed speech. To tackle the problem, we take conventional-vocoder-generated speech as the reference speech to derive a linear predictive coding distribution constraint (LPCDC) to avoid the collapsed speech problem. Furthermore, to mitigate the negative effects introduced by the LPCDC, we propose a collapsed speech segment detector (CSSD) to ensure that the LPCDC is only applied to the problematic segments to limit the loss of quality to short periods. Objective and subjective evaluations are conducted, and the experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, which further improves the speech quality of our previous non-parallel VC system submitted to Voice Conversion Challenge 2018.
Conclusion
In this paper, we explored the phenomena, possible reasons, and negative effects of the collapsed speech problem of the WN vocoder. We also proposed the LPCDC technique to protect the WN vocoder from the collapsed speech problem, but it caused extra speech quality degradation. Therefore, we applied the CSSD to segmentally detect the collapsed speech and applied the LPCDC technique to only the detected segments, which greatly alleviated the speech degradation problem. To summarize, we proposed a system outperforming the previous system submitted to VCC2018.