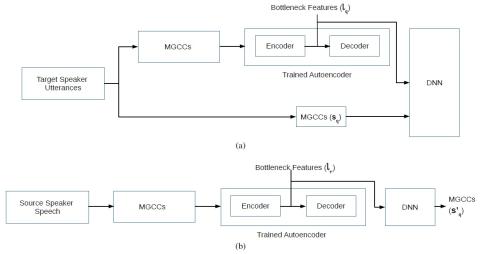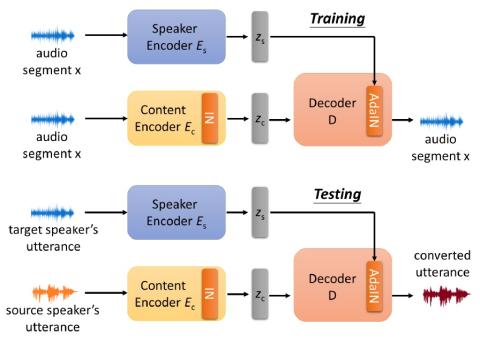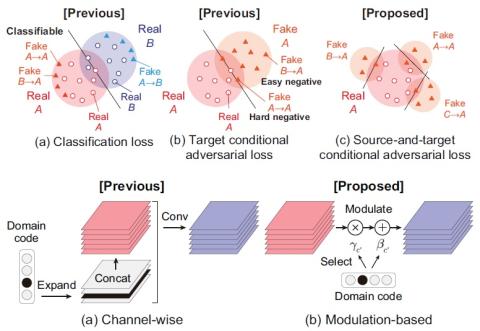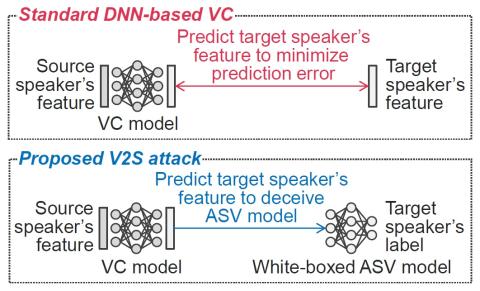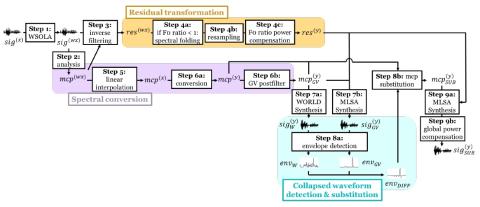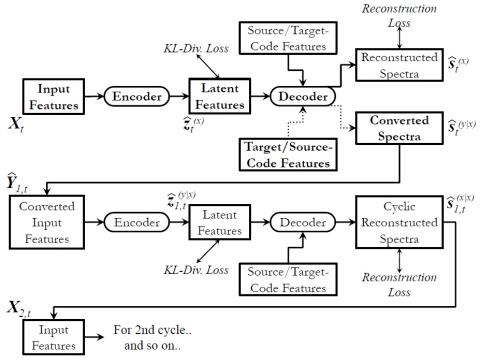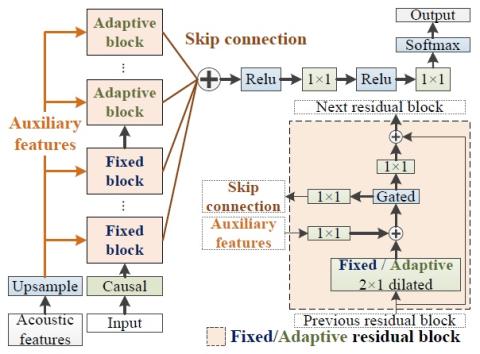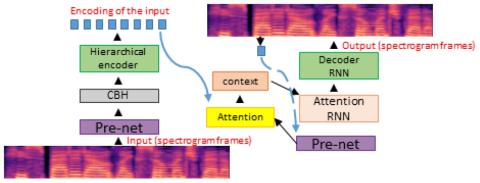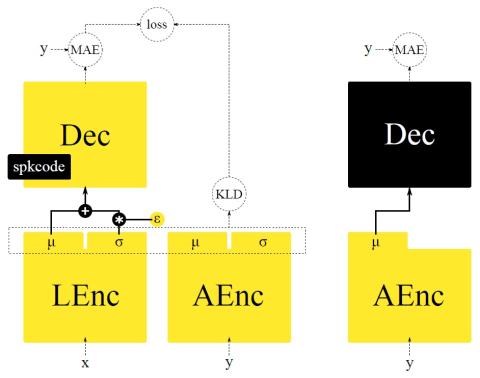
Bootstrapping non-parallel voice conversion from speaker-adaptive text-to-speech
Voice conversion (VC) and text-to-speech (TTS) are two tasks that share a similar objective, generating speech with a target voice. However, they are usually developed independently under vastly different frameworks. In this paper, we propose a methodology to bootstrap a VC system from a pretrained speaker-adaptive TTS model and unify the techniques as well as the interpretations of these two tasks. Moreover by offloading the heavy data demand to the training stage of the TTS model, our VC system can be built using a small amount of target speaker speech data. It also opens up the possibility ...