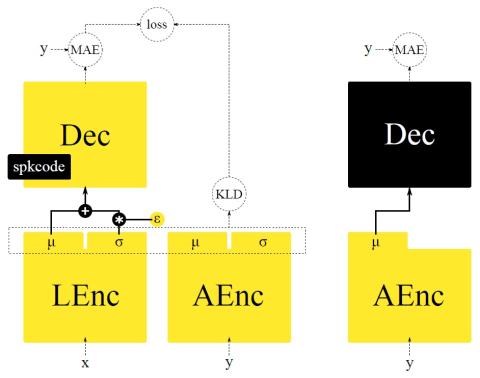
Voice conversion (VC) and text-to-speech (TTS) are two tasks that share a similar objective, generating speech with a target voice. However, they are usually developed independently under vastly different frameworks. In this paper, we propose a methodology to bootstrap a VC system from a pretrained speaker-adaptive TTS model and unify the techniques as well as the interpretations of these two tasks. Moreover by offloading the heavy data demand to the training stage of the TTS model, our VC system can be built using a small amount of target speaker speech data. It also opens up the possibility of using speech in a foreign unseen language to build the system. Our subjective evaluations show that the proposed framework is able to not only achieve competitive performance in the standard intra-language scenario but also adapt and convert using speech utterances in an unseen language.
Conclusion
In this paper, we have presented a methodology to bootstrap a VC system from a pretrained speaker-adaptive TTS model. By transferring knowledge learned previously by the TTS model, we were able to significantly lower the data requirements for building the VC system. This in turn allows the system to operate in a low-resource unseen language. The subjective results show that our VC system achieves competitive performance compared with existing methods. Moreover, it can also be used for cross-language voice conversion and cross-language speaker adaptation. While the performance in these unseen language scenarios are not as good, all experiments in this work are conducted under the assumption of minimal available resources. Our future work includes taking advantage of the available additional resources such as a multi-lingual corpus to further improve the robustness of the VC system.