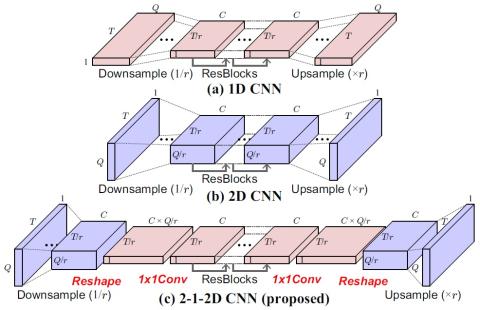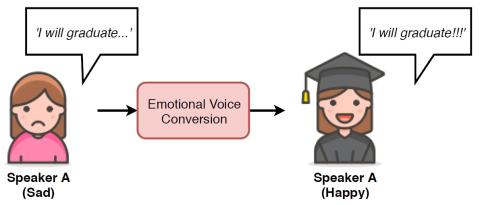
Transforming Spectrum and Prosody for Emotional Voice Conversion with Non-Parallel Training Data
Emotional voice conversion is to convert the spectrum and prosody to change the emotional patterns of speech, while preserving the speaker identity and linguistic content. Many studies require parallel speech data between different emotional patterns, which is not practical in real life. Moreover, they often model the conversion of fundamental frequency (F0) with a simple linear transform. As F0 is a key aspect of intonation that is hierarchical in nature, we believe that it is more adequate to model F0 in different temporal scales by using wavelet transform. We propose a CycleGAN network to f...