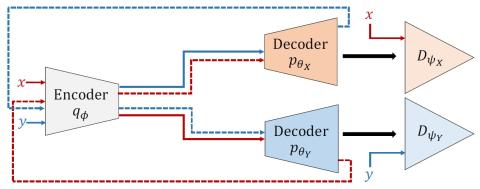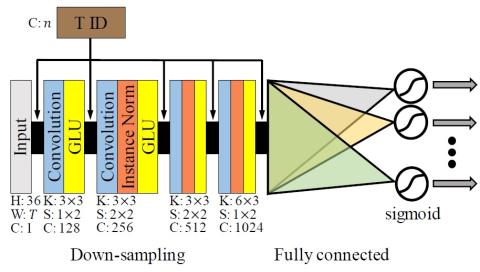
Many-to-Many Voice Conversion using Conditional Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
Voice conversion (VC) refers to transforming the speaker characteristics of an utterance without altering its linguistic contents. Many works on voice conversion require to have parallel training data that is highly expensive to acquire. Recently, the cycle-consistent adversarial network (CycleGAN), which does not require parallel training data, has been applied to voice conversion, showing the state-of-the-art performance. The CycleGAN based voice conversion, however, can be used only for a pair of speakers, i.e., one-to-one voice conversion between two speakers. In this paper, we extend the ...