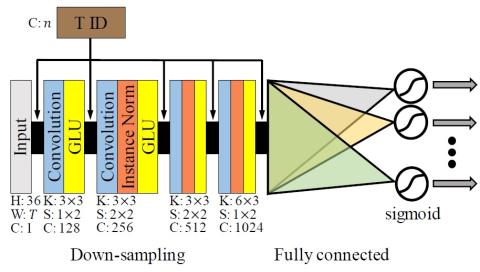
Voice conversion (VC) refers to transforming the speaker characteristics of an utterance without altering its linguistic contents. Many works on voice conversion require to have parallel training data that is highly expensive to acquire. Recently, the cycle-consistent adversarial network (CycleGAN), which does not require parallel training data, has been applied to voice conversion, showing the state-of-the-art performance. The CycleGAN based voice conversion, however, can be used only for a pair of speakers, i.e., one-to-one voice conversion between two speakers. In this paper, we extend the CycleGAN by conditioning the network on speakers. As a result, the proposed method can perform many-to-many voice conversion among multiple speakers using a single generative adversarial network (GAN). Compared to building multiple CycleGANs for each pair of speakers, the proposed method reduces the computational and spatial cost significantly without compromising the sound quality of the converted voice. Experimental results using the VCC2018 corpus confirm the efficiency of the proposed method.
Conclusions
We proposed a novel many-to-many non-parallel voice conversion method called the CC-GAN based VC. It uses only a single GAN for many-to-many voice conversion while the CycleGAN based VC would require 𝑛(𝑛−1) GANs for 𝑛 speakers. As a result, the CC-GAN based VC decreases the training time significantly as well as the model size for many-to-many voice conversion. We showed experimentally that the proposed method was comparable to the CycleGAN based VC which shows the state-of-the-art performance for one-to-one non-parallel voice conversion without using any extra modules such as ASR systems. To the best of our knowledge it is the first work that shows the feasibility of the extension of the CycleGAN for many-to-many voice conversion using 12 speakers.