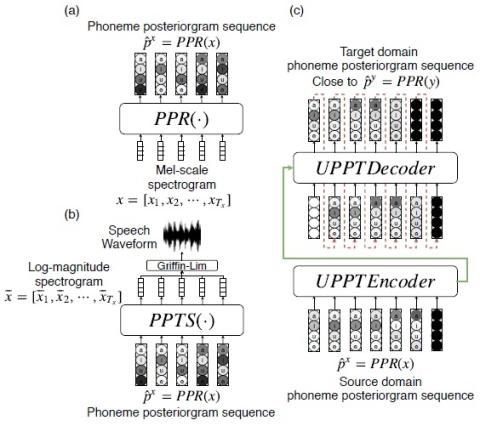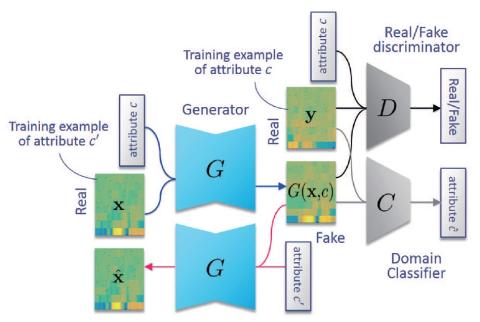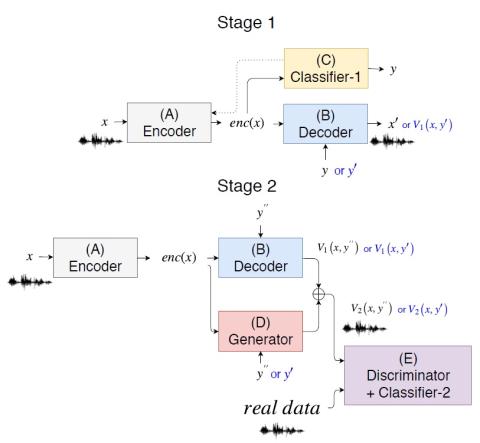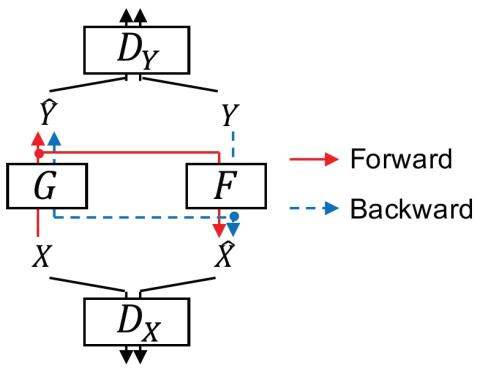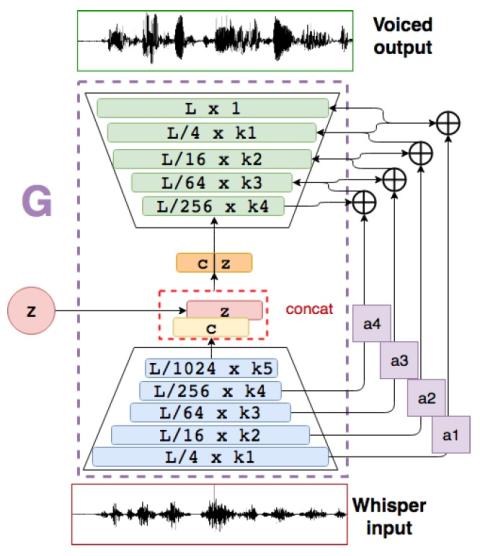
Whispered-to-voiced Alaryngeal Speech Conversion with Generative Adversarial Networks
Most methods of voice restoration for patients suffering from aphonia either produce whispered or monotone speech. Apart from intelligibility, this type of speech lacks expressiveness and naturalness due to the absence of pitch (whispered speech) or artificial generation of it (monotone speech). Existing techniques to restore prosodic information typically combine a vocoder, which parameterises the speech signal, with machine learning techniques that predict prosodic information. In contrast, this paper describes an end-to-end neural approach for estimating a fully-voiced speech waveform from ...